LiFePO4 Battery
Polymer Lithium Battery: Features, Benefits, and Drawbacks
Table of Contents
What Is a Polymer Lithium Battery?
A polymer lithium battery uses polymer materials as the electrolyte. Manufacturers classify them into semi-polymer and full-polymer.
-
Semi-polymer: A polymer layer, often PVDF, coats the separator. This design strengthens adhesion and allows the battery to become more rigid, while the electrolyte remains liquid.
-
Full-polymer: Inside the cell, polymers form a gel network, and then liquid electrolyte is injected. Although it still contains liquid, the volume is much lower, which significantly improves safety. For example, SONY is one of the few companies producing full-polymer lithium batteries on a large scale.
In addition, the term “polymer battery” often refers to soft-pack batteries that use aluminum-plastic film packaging instead of rigid metal cases.
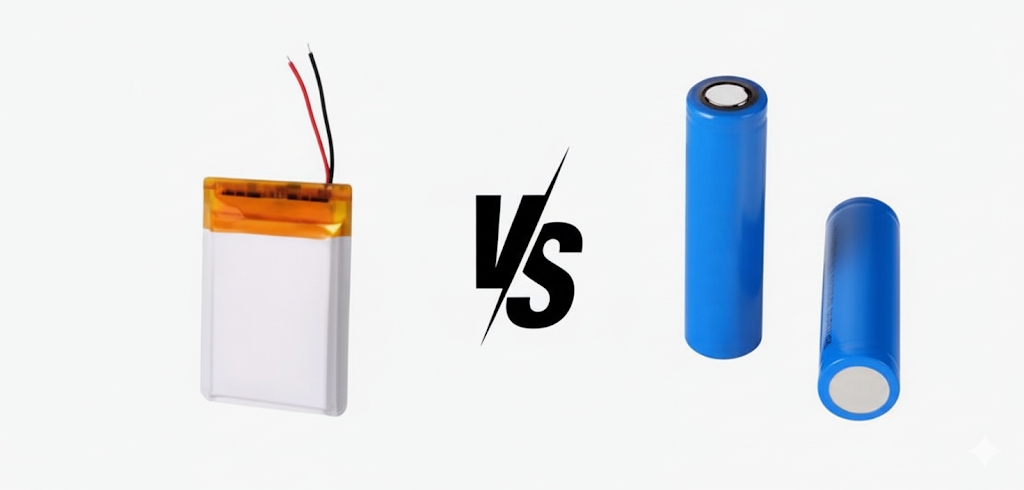
Differences Between Lithium-Ion and Polymer Lithium Batteries
-
Materials
-
Lithium-ion batteries use liquid or gel electrolytes.
-
Polymer lithium batteries use polymer electrolytes in solid or gel form combined with organic liquid electrolytes.
-
-
Safety
-
Lithium-ion batteries can explode under extreme heat or pressure.
-
Polymer lithium batteries, using aluminum-plastic casings, are safer. In case of failure, they may swell or burn but are less likely to explode.
-
-
Form Factor
-
Polymer batteries can be made ultra-thin and shaped freely.
-
Lithium-ion cells require rigid casings, limiting design flexibility.
-
-
Voltage
-
Polymer batteries can achieve higher voltages through layered designs.
-
Standard lithium-ion cells provide 3.6V and need to be connected in series to reach higher voltages.
-
-
Manufacturing
-
Thinner polymer cells are easier to manufacture.
-
Thicker lithium-ion cells are simpler for large-scale production.
-
-
Capacity
-
Polymer lithium batteries generally do not provide higher capacity compared to standard cylindrical lithium cells.
-
Advantages of Polymer Lithium Batteries
-
High Safety: With flexible aluminum-plastic packaging, they are less prone to explosions compared to metal-cased cells.
-
Thin Design: Can be made less than 1mm thick, ideal for compact electronics such as credit card-sized devices.
-
Lightweight: Up to 40% lighter than steel-cased lithium batteries.
-
Customizable Shapes: Can be tailored to fit specific product designs, maximizing space utilization.
Limitations of Polymer Lithium Batteries
-
Higher Cost: Custom designs increase R&D and production expenses.
-
Low Interchangeability: Unique designs reduce standardization and compatibility.
-
Shorter Lifespan: Compared with 18650 cylindrical cells, polymer lithium batteries may have reduced cycle life under high current discharge.
-
All-or-Nothing Replacement: If damaged, the entire pack often needs to be replaced.


Featured Forklift LiFePo4 Battery
80V Forklift Battery
Forklift Lithium-ion Battery 80v 404Ah for Toyota 7FB30-7FBJ35
48V Forklift Battery
Forklift Lithium Battery 51.2v 404Ah for Still FM-X
48V Forklift Battery
48V 519Ah Lifepo4 Lithium Battery for Heli CPD20/25-GB2/GD Forklift
80V Forklift Battery
80V 404Ah Lifepo4 Lithium Battery for CPD30/35-G1/G3 Forklift
80V Forklift Battery
80V 560AH Lifepo4 Lithium Battery for HELI CPD35-GD2
80V Forklift Battery
80V 600Ah LiFePO4 Lithium Battery for NICHIYU FBC25/30P Forklift
48V Forklift Battery
48V 201Ah Lifepo4 Lithium Battery for NICHIYU FBRM13H-70 Reach Truck
48V Forklift Battery
48V 225Ah Lifepo4 Lithium Battery for HYUNDAI 10/13BR Forklift